Sculpting Digital Realms: The Role of a 3D Modeler in 3D Animation
Sculpting Digital Realms: The Role of a 3D Modeler in 3D Animation
Introduction
In the dynamic world of 3D animation and digital visualization, the creation of lifelike characters, environments, and objects is a meticulous and creative process led by skilled professionals known as 3D modelers. These artists are the architects of the digital realm, shaping and sculpting virtual entities that come to life on screens both large and small. This article explores the essential role of a 3D modeler, examining their responsibilities, the tools of their trade, and the captivating artistry that defines their craft.
Defining a 3D Modeler
A 3D modeler is an artist who specializes in creating three-dimensional digital models of objects, characters, or environments. These models serve as the foundation for 3D animations, video games, virtual reality experiences, and more. Utilizing specialized software, 3D modelers bring concepts and designs to life in a dynamic and immersive space, adding depth, texture, and realism to the virtual world.

Key Responsibilities of a 3D Modeler
-
Conceptualization: Collaborating closely with directors, art directors, and other creative stakeholders, 3D modelers begin their process by understanding the vision and design requirements for the project.
-
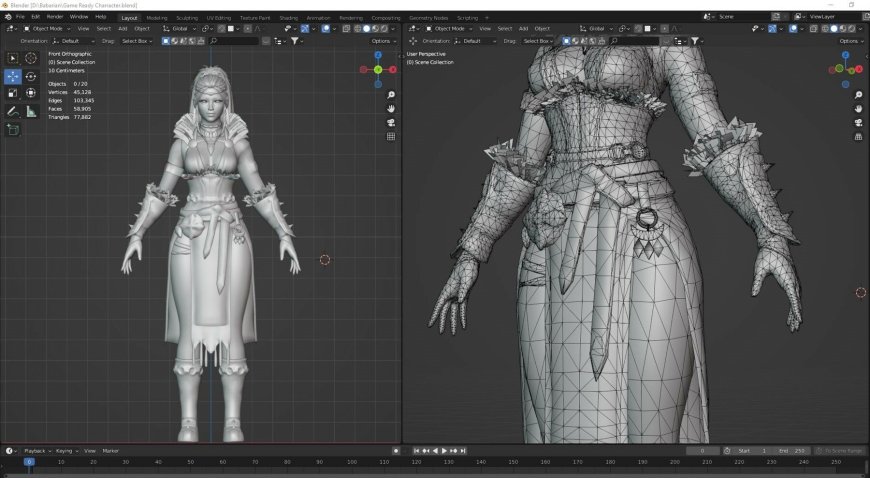
Modeling: The core responsibility of a 3D modeler is to create digital representations of objects or characters. Using specialized modeling software, these artists sculpt, shape, and refine the geometry of the 3D model to match the intended design.
-
Texturing: Texturing involves applying surface details, colors, and materials to the 3D model to enhance its visual appeal and realism. 3D modelers work with texture artists to ensure that surfaces look lifelike and convey the intended visual aesthetic.
-
Lighting and Shading: Collaborating with lighting and shading artists, 3D modelers contribute to the creation of realistic lighting effects, shadows, and reflections that enhance the overall visual quality of the digital scene.
-
Rigging Consultation: While rigging is typically the responsibility of other specialists, 3D modelers often collaborate with rigging artists to ensure that the models are designed in a way that allows for realistic movement during animation.
-
Animation Feedback: During the animation process, 3D modelers may provide feedback and adjustments to ensure that the models deform and move naturally, maintaining visual integrity throughout various poses and movements.
-
Quality Control: 3D modelers are responsible for ensuring that the final product meets the quality standards set by the project. This involves reviewing models, textures, and overall visual elements for consistency and accuracy.
Artistry of a 3D Modeler
The artistry of a 3D modeler lies in their ability to translate 2D concepts or ideas into intricate and tangible three-dimensional forms. It requires a keen eye for detail, an understanding of spatial relationships, and a mastery of the tools and techniques employed in 3D modeling software.
Each curve, edge, and texture applied by a 3D modeler contributes to the overall visual language of the project. Their artistry is not merely technical but also deeply creative, as they breathe life into the digital entities that populate virtual worlds.
Conclusion
In the realm of 3D animation and digital visualization, 3D modelers are the architects who sculpt the foundations of virtual realities. Their artistry is instrumental in creating visually stunning and immersive experiences, enriching the storytelling process and captivating audiences worldwide. The next time you find yourself marveling at the lifelike characters or intricately designed environments in a 3D animated film or video game, take a moment to appreciate the craftsmanship of the 3D modelers who shape the digital landscapes we explore and enjoy.